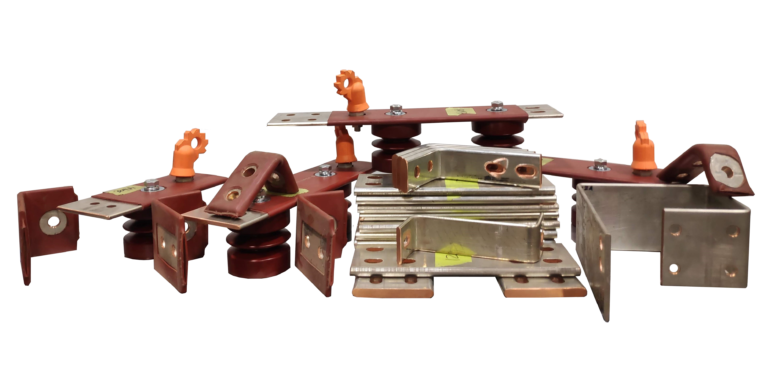
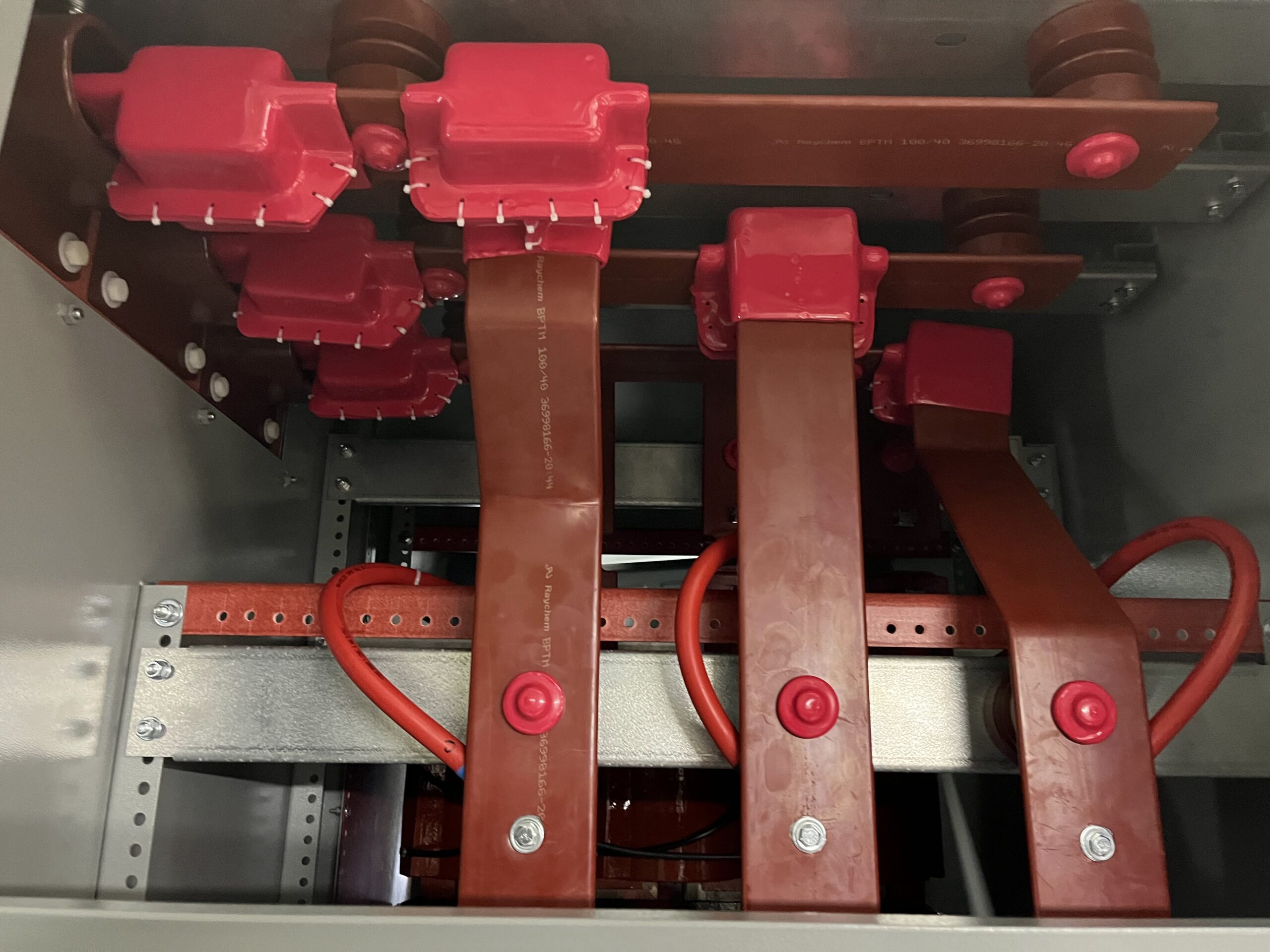
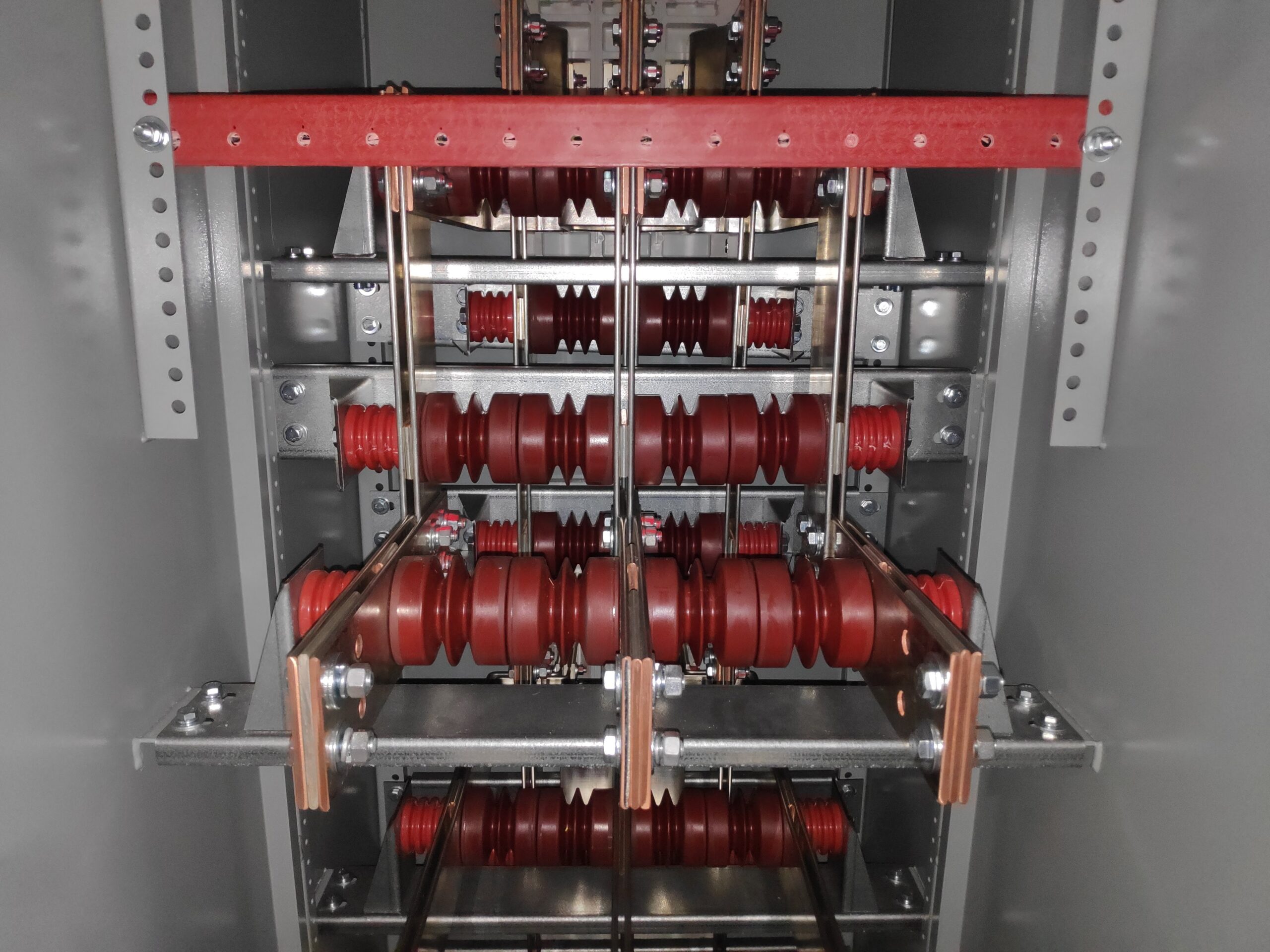
Busbar Fabrication Services
Busbar fabrication involves precisely manufacturing copper or aluminum bars designed to conduct electrical current efficiently and to fit in the given or intended design. Fabrication includes cutting, punching, bending, and plating to ensure the bus bars meet specific design and performance requirements. Depending on the application, we customize fabrication to accommodate various sizes, shapes, and current capacities. Proper insulation and coating are often applied to enhance safety and prevent corrosion. At Solution Controls, we use advanced techniques to fabricate high-quality bus bars that ensure optimal conductivity, durability, and reliability for various electrical systems.
Busbar Fabrication Process
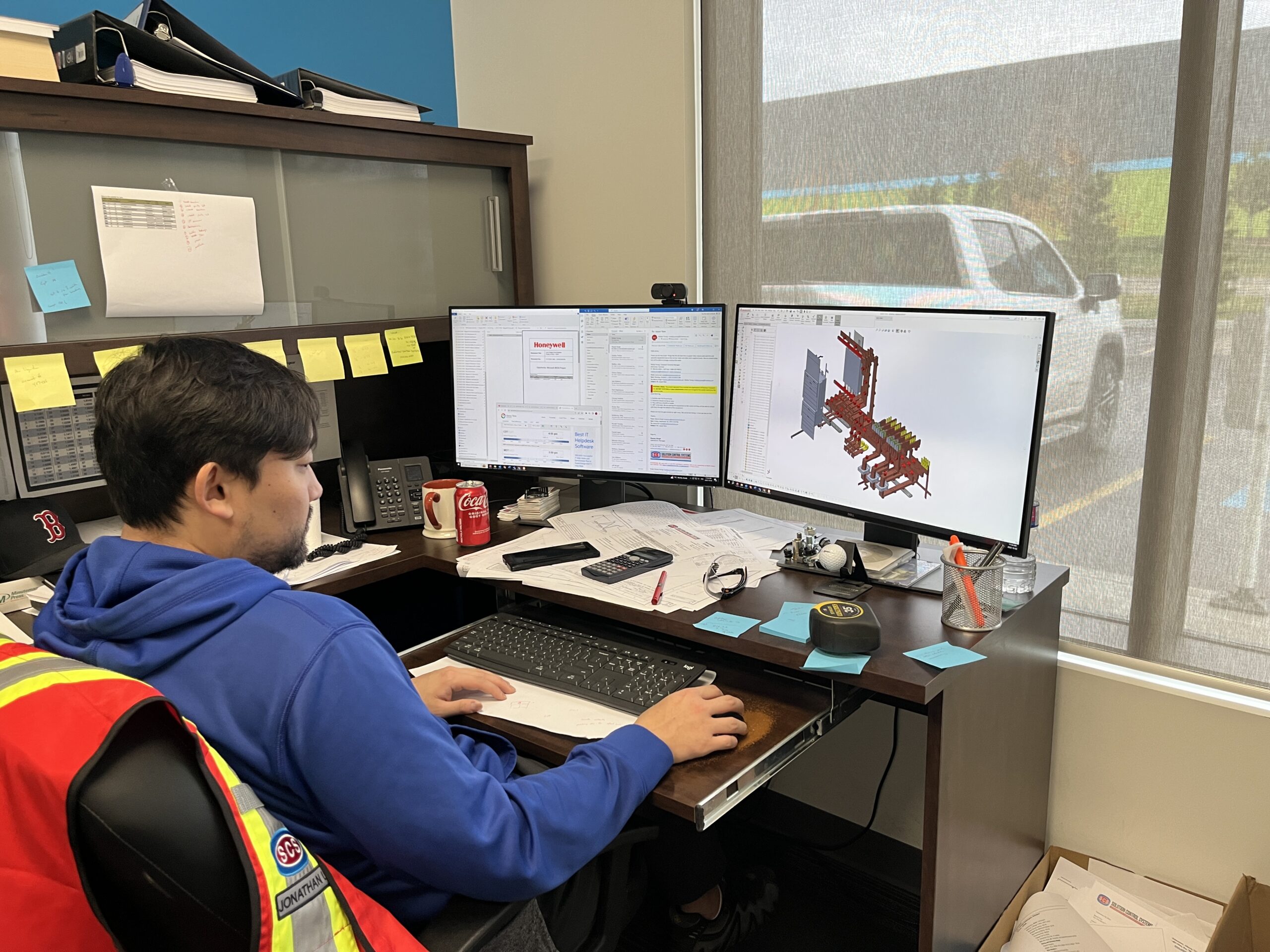
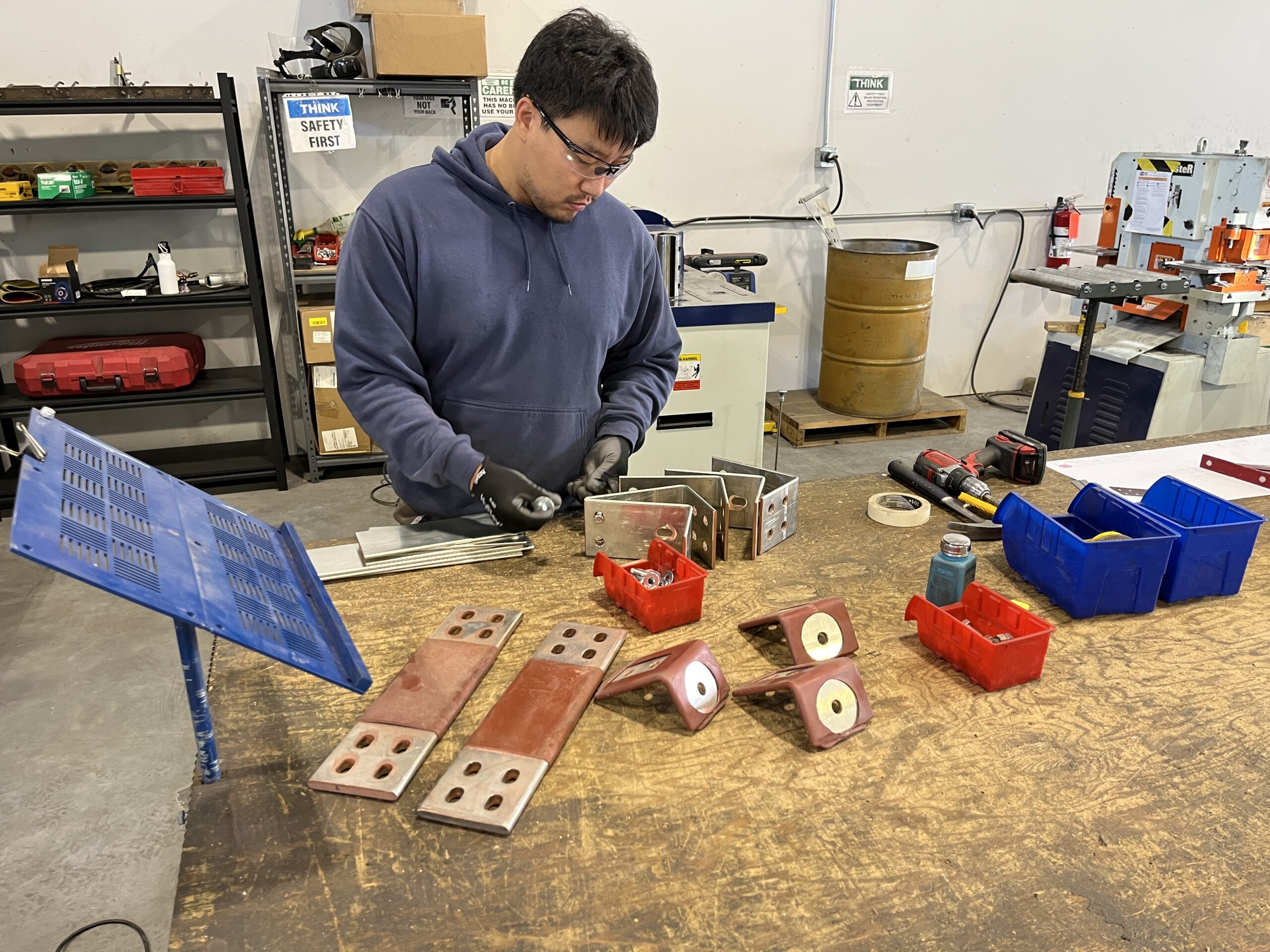
Our busbars are designed in solid works, offering customers a detailed visual representation of the final product. This allows for fit testing without the need for physical components and ensures precise specifications for fabrication, capturing every fine detail.
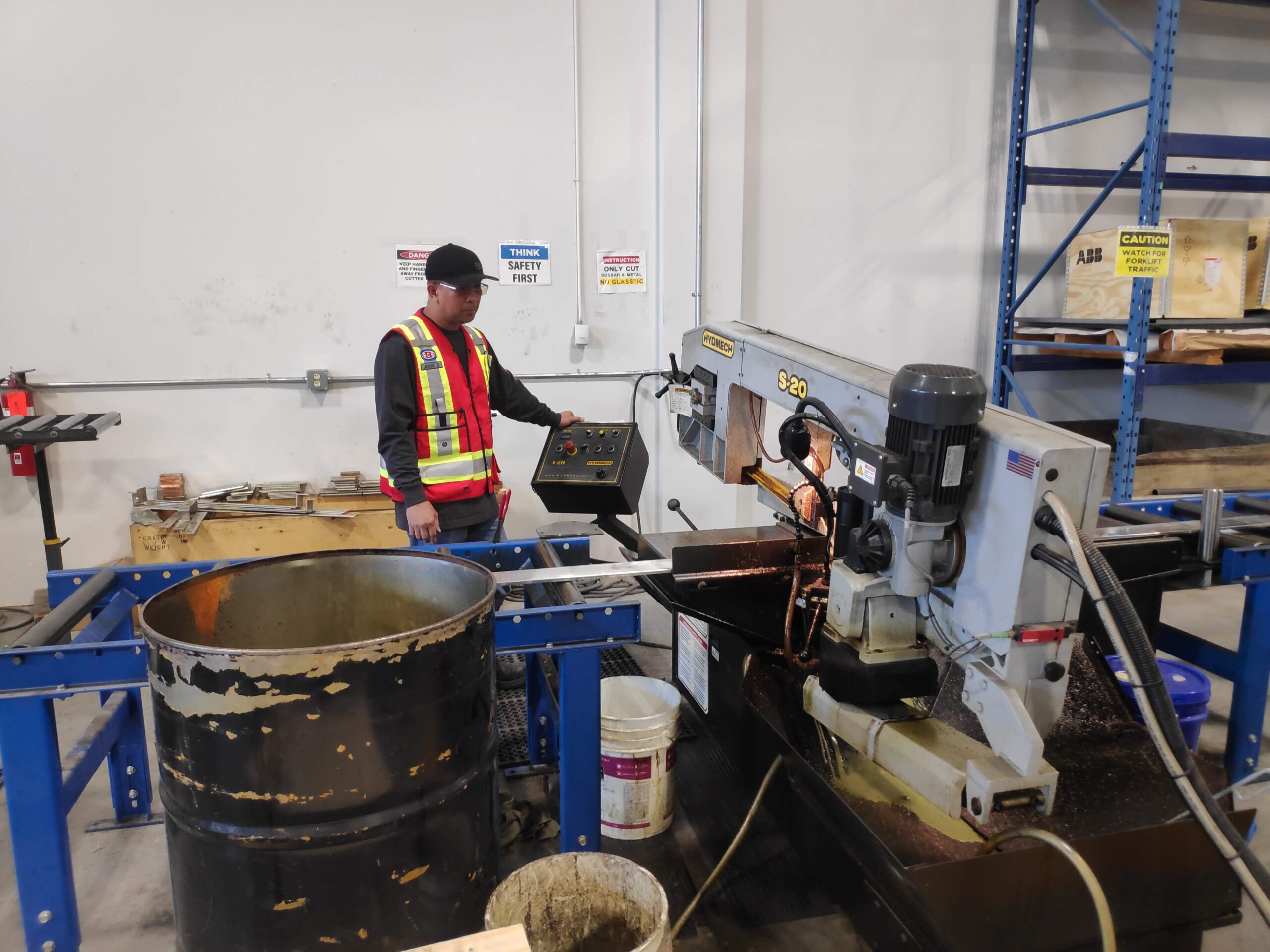
Our busbars are cut using a floor-mounted Hydmech band saw, a semi-automatic, variable-speed horizontal pivot saw. This auto-feed machine delivers high-precision cuts on various metals, including copper and steel, without constant supervision. The integrated coolant system enhances blade longevity and ensures clean, accurate cuts.
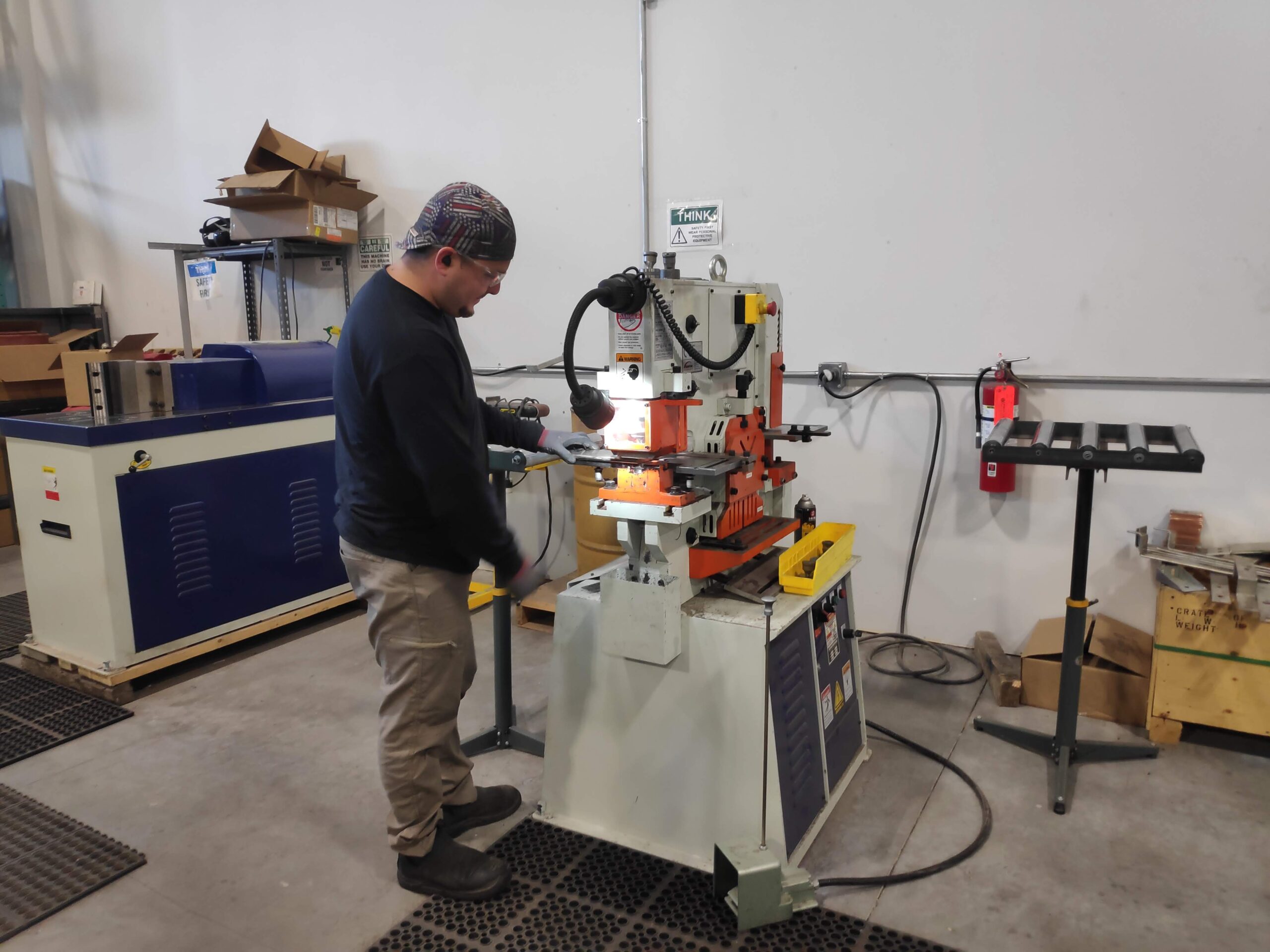
Our busbars are punched using a 50-ton Fabmaster hydraulic punch machine, capable of handling a variety of punch shapes, including round, oval, and square holes. In addition to busbar punching, this versatile machine can shear flat metal, square tubing, rods, and perform flat piece notching, with the potential for even more applications using additional accessories.
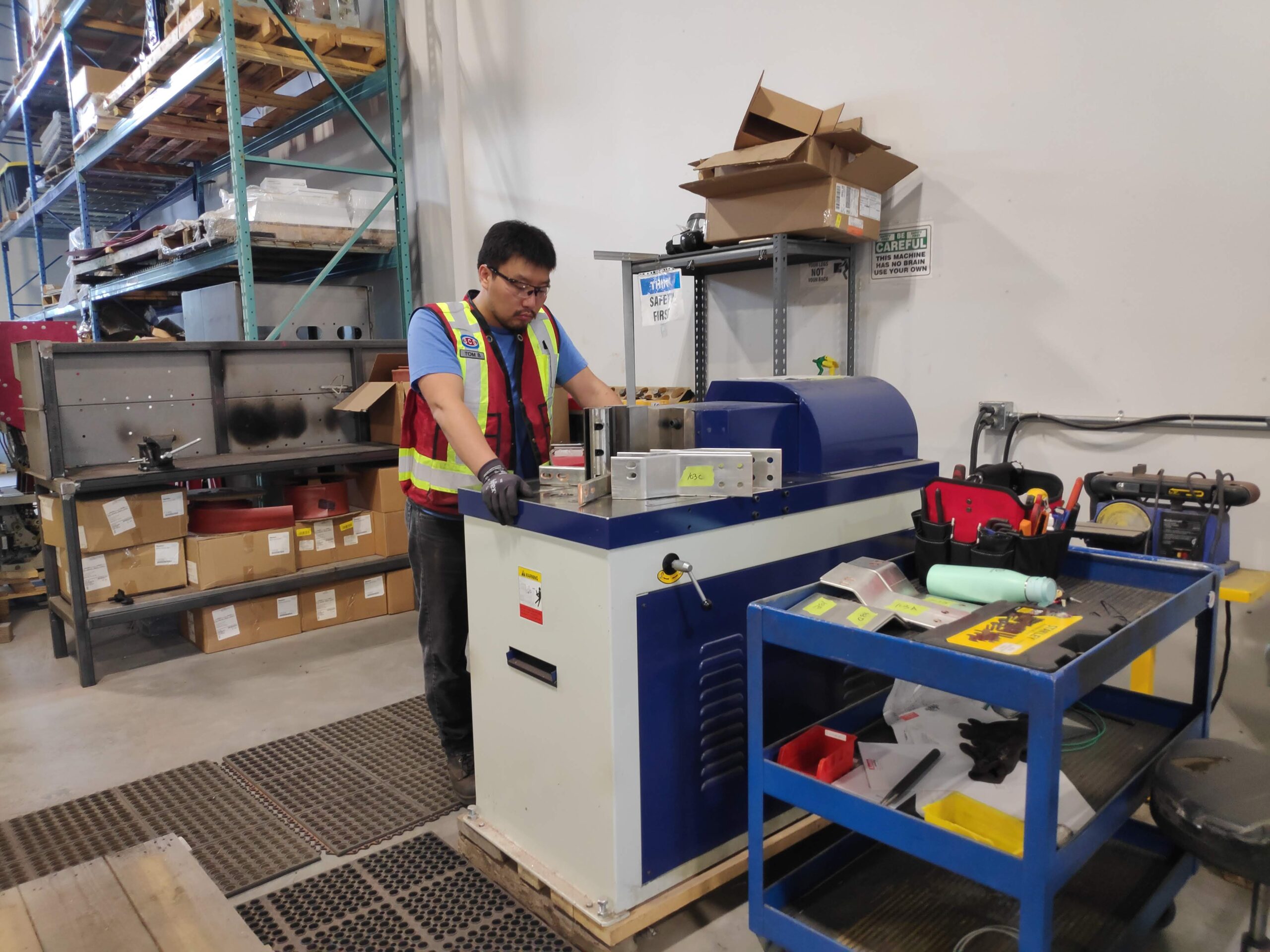
Our busbars are bent using a 50-ton Sunrise hydraulic bending machine, capable of bending up to 6" x 1/2" busbars. This high-quality, reliable hydraulic metalworking machine offers a wide range of tooling for various bending operations, and we also customize special tooling to meet specific project requirements.
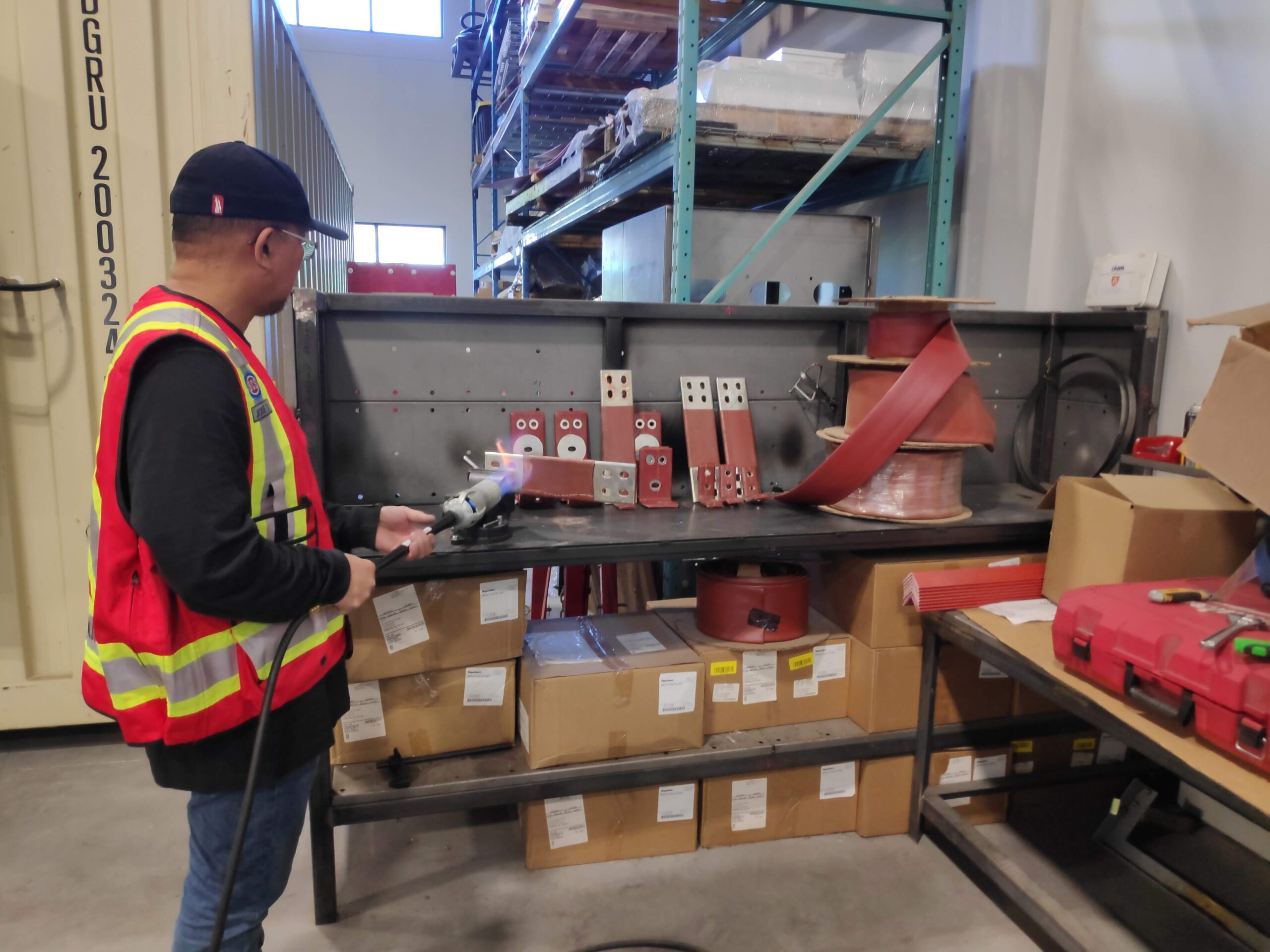
Our busbars are heat-shrunk for medium-voltage applications, ensuring proper insulation. The process involves sliding the appropriately sized shrink tubing onto the busbar, heat shrinking it using an open-flame torch, and precisely cutting the tubing for insulator or hardware placement.
The insulated busbars are installed inside a gear cell, with bus-to-bus connections securely mounted on insulators and the supporting structure. Each bus connection is protected with custom-fitted bus boots, ensuring proper insulation and safety for all connection points.
Multiple busbar pieces are installed in this low-voltage breaker section. The side busbars are mounted on enclosure supports with insulators, while the center busbar is securely mounted on insulators from both sides, ensuring stability and proper insulation.
What is a Busbar?
Busbars are vital components in electrical systems. They consist of copper or aluminum strips or bars that conduct steady electrical current. At Solution Controls, we primarily use copper busbars for fabrication but are fully equipped to fabricate with aluminum as needed. Busbars ensure reliable and efficient power distribution across various system loads. Designed to accommodate multiple current capacities, they offer operational flexibility without modifying other system components. Their advantages include the capacity to carry large amounts of current, improved safety, and enhanced cost efficiency.
Types of Busbars
Single Busbar System
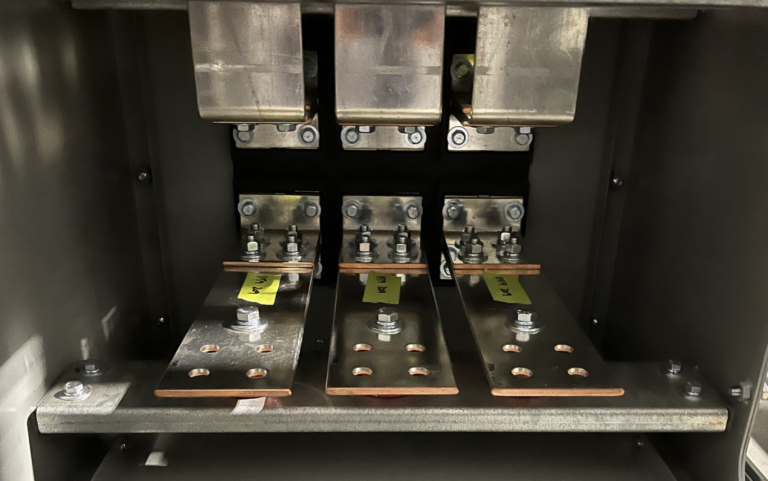

A single busbar system features a simple design, directly connecting all switches and circuits. The configuration is cost-effective and easy to maintain, making it ideal for less complex installations where high flexibility and redundancy are not required.
Double or Multilayer Busbar System
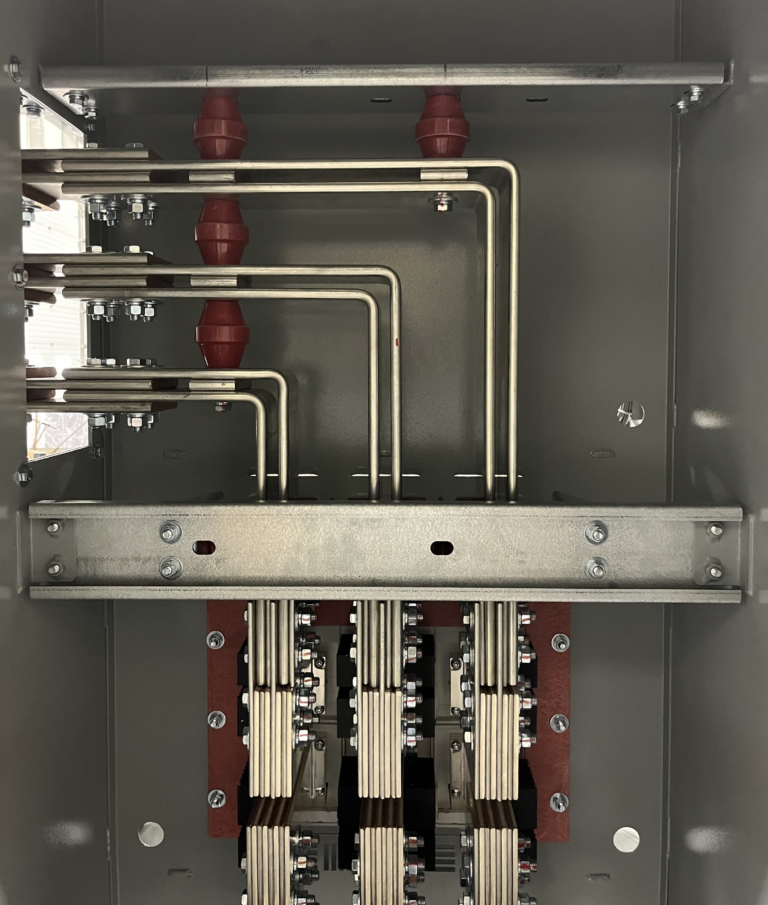
A double busbar system incorporates two parallel busbars, making it suitable for environments where uninterrupted power supply is critical. This configuration provides operational flexibility by allowing circuits to be transferred between busbars without disrupting the power flow. While it enhances system reliability and reduces the risk of outages, it also comes with trade-offs, such as increased complexity, higher costs, and greater space requirements.
Insulated Busbar System
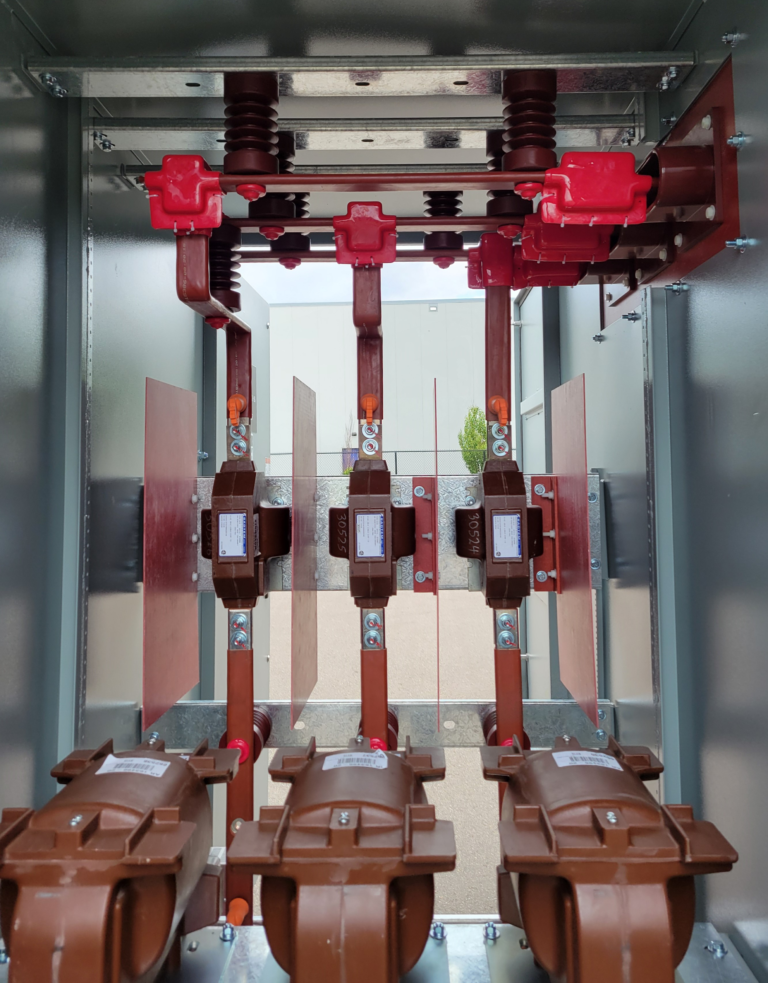

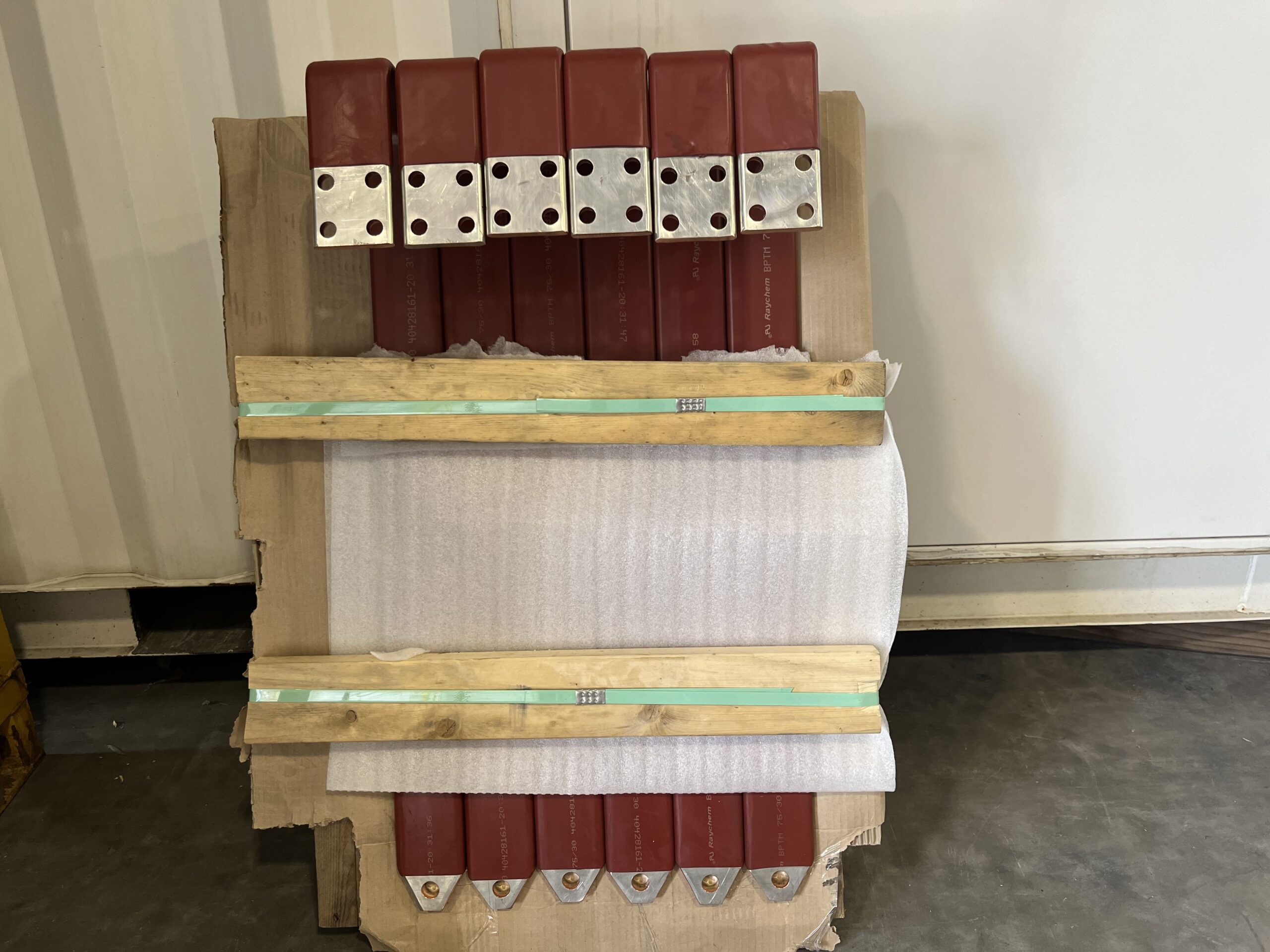
The busbars are installed in medium voltage switch gear systems operating at voltages from 5KV – 38KV. Each busbar piece is individually covered with high-grade, high-class insulation materials. The insulation not only prevents electrical arcing but also protects the system from short circuits and unwanted ground faults. The insulation is carefully cut around mounting holes and connection points, allowing for precise attachment to other components within the switchgear. After final assembly bus boots are installed over the bare and exposed connections of the busbar. The bus boots are designed to fully cover the joints and connection points where the busbar interfaces with other components or connectors.
Material used for Busbar
Busbars are metallic conductors that serve as a central hub for multiple electrical connections. The bars are made from various materials, but the two most common are copper and aluminum. Both copper and aluminum have unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on the project's specific needs and requirements.
- Copper Busbar - At Solution Control Systems, we utilize copper busbars due to their superior conductivity, strength, and durability. Copper's excellent electrical performance and heat dissipation make it an ideal choice for high-power applications, ensuring reliable and efficient power distribution. Our copper busbars are custom-fabricated to meet each project's unique needs, offering both flexibility and long-term reliability in demanding electrical systems.
- Aluminum Busbar - Although Solution Controls primarily uses copper busbars, we can fabricate with aluminum as needed. The strength, conductivity, and capability of aluminum depend on the alloying agents used. Aluminum’s characteristics range from incredibly soft to firm, like mild steel.
Busbar Applications and Capabilities
Busbars are essential components in electrical power distribution systems, used to efficiently conduct and distribute electricity in switchgear, substations, panel boards, and other electrical apparatus. They can handle high current loads and are commonly found in oil and gas plants, utility and power generation facilities, renewable energy systems, agriculture, mining plants, forestry/pulp and paper and manufacturing facilities. Their versatility allows for easy customization in terms of size, shape, and material, enabling optimized performance across medium to high-voltage applications while minimizing energy loss and improving system reliability.
Typical Applications
Busbars are widely used in switchgears, busways, and power distribution panels, often referred to as splitter boxes or troughs. They provide an efficient solution for interconnecting circuit breakers, load break switches, transformers, capacitor banks, and UPS systems based on application requirements. Busbar pads are also frequently utilized for field cable connections.
Busbar Capabilities
Busbars are versatile electrical components designed for efficient power distribution. They handle high current loads, offer superior heat dissipation, and support various configurations. Their robust construction ensures safety during short-circuit events, while their clean design enhances system organization and aesthetics.
Role of Busbars in Switchgear
Busbars are primary conductors connecting breakers, switches, and other components capable of handling high currents. They are essential in electrical distribution systems as they facilitate the safe and efficient transfer of electricity between multiple components. Switchgears require a high short-circuit rating, and due to their robust characteristics, busbars can achieve these high short-circuit ratings, ensuring the system's stability and safety during fault conditions. Additionally, their design allows for better heat dissipation and reduces the risk of overheating, making them a reliable choice for high-demand applications. This combination of strength, efficiency, and heat management makes busbars a critical component in modern electrical infrastructure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Busbars
Advantages
- Reliable for reliably handling and distributing high current loads.
- Achieves robust protection against short-circuit conditions.
- Provides a clean and organized appearance for electrical systems.
- Sections can be easily detached at shipping splits, facilitating convenient transportation.
- Effectively manages higher current loads while minimizing the risk of overheating.
Disadvantages
- Requires thorough planning and design before fabrication and installation.
- Require specific tools and training for proper installation.
- Requires adequate spacing because of exposed surfaces.
- Requires significantly more time for both fabrication and insulation.